By Ashley Dean and Erin Hodgson
Corn rootworm egg hatch in Iowa typically occurs from late May to the middle of June, with an average peak hatching date of June 6 in central Iowa. Even with recent warm temperatures, hatching is a bit delayed this year due to cool spring temperatures. Development is driven by soil temperature and measured by growing degree days (GDDs). Research suggests about 50% of egg hatch occurs between 684-767 accumulated GDDs (since January 1; base 52°F, soil). Many areas have reached peak corn rootworm egg hatch, and the northern portion of the state could experience peak hatch within a week (Figure 1).
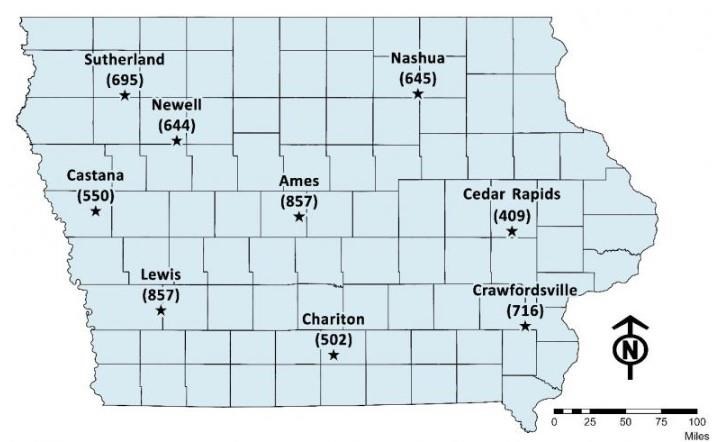
Figure 1. Accumulated soil degree days (base 52°F) in Iowa as of June 20, 2022. Expect 50% egg hatch of corn rootworm between 684-767 degree days.
To predict corn rootworm egg hatch for your area based on degree day accumulation, use the Iowa State Agronomy Environmental Mesonet website. Set the start date to January 1 of the current year, use the current date for the end date, and make sure the plot parameter is set to “soil growing degree days (base = 52).”
A severe corn rootworm larval infestation can destroy nodes 4-6; each node has approximately 10 nodal roots. Root pruning interferes with water and nutrient uptake and makes the plant unstable (Figure 2). Recent research predicts a 15% yield loss for every node pruned back to 1 ½ inches. Prolonged drought can exacerbate root injury and cause additional yield loss.
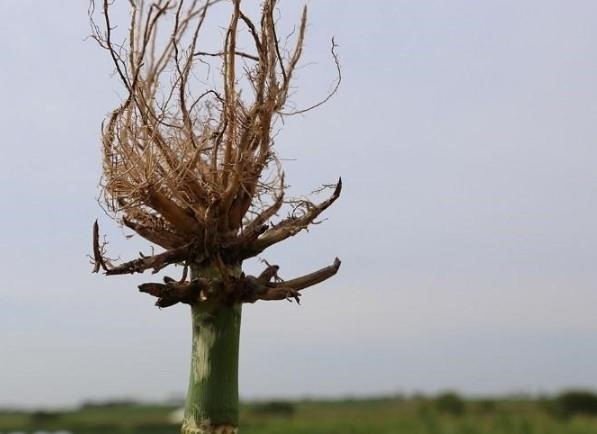

Figure 2. Severe root pruning by corn rootworm larvae can dramatically impact yield.
Regardless of agronomic practices used to suppress corn rootworm (e.g., crop rotation, Bt hybrids, or soil-applied insecticides), every corn field should be scouted for corn rootworm root injury. Continuous corn fields and areas with Bt trait performance issues are the highest priority for inspection. It is ideal to look at corn roots 10-14 days after peak egg hatch because the feeding injury will be fresh. On some hybrids, corn roots can grow back and make it difficult to assess feeding injury later in the season. Assess corn rootworm feeding and adjust management strategies if the average injury is above 0.5 on the ISU 0 to 3 Node Injury Scale. Also consider monitoring for adult corn rootworm to supplement root injury assessments.
To refresh your root injury assessment skills, consider attending one of the seven corn rootworm demonstrations occurring in Iowa this summer.
Source : iastate.edu