Correlation of Soil ECa and Crop Yield
Soil ECa has shown a good correlation with soil properties that affect crop productivity and yield. After precision farmers create yield maps and conduct a preliminary evaluation of the yield response, they will identify the manageable causes of crop yield response.
Differences in soil properties are the most-apparent reasons for yield variability. Soil ECa has the potential to estimate variations in some soil physical properties in a field, and yield maps are frequently correlated to soil ECa (Figure 3).
Based on ECa data, sandy soils with low organic matter have low EC, silts have medium and clays have higher EC (Figure 4).
ECa data are often validated by soil sampling and yield data to determine an accurate variable rate of inputs.

Figure 3. Aerial imagery, EC data and the yield data for a field have a good correlation. If the data and information are collected correctly, any one of these can give you an idea about your field conditions.
In many situations, these similarities are explained through differences in soil. The soil's water-holding capacity is a major factor affecting yield, and the yield map will likely show a strong correlation to the soil ECa. In general, soil ECa maps may indicate areas where further exploration is needed.
Most likely, soil ECa maps give valuable information about soil variations and similarities, making it possible to divide the field into smaller management zones. Zones with consistent ECa readings are areas with similar soil properties and may be grouped together for soil sampling and management.
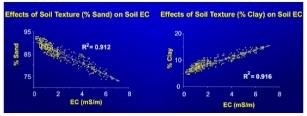
Figure 4. Soil EC is a way to measure soil texture, sand, silt and clay. The finer particles of clay conduct more electricity than coarser silt and sand particles. Thus, higher clay results in higher EC, while higher sand results in lower EC.
Application of Soil EC Maps
- Identifying management zones, generating prescription maps and decision support.
- A better interpretation of yield maps and improving prescription maps.
- Weed and diseases management (less herbicide in sandy soils and identifying disease outbreak areas).
- Tillage, drainage and irrigation decisions.
- Research and plot work improvement.