A tick saliva study reveals immune responses that could lead to better protection for cattle.
Scientists from Hokkaido University, Japan and Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul and Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, have revealed that substances in tick saliva activates immune response-suppressing proteins in cattle that facilitates the transmission of tick-borne diseases. The finding was published in the journal Scientific Reports and could help in the development of alternative control strategies.
The Asian blue tick, Rhipicephalus microplus, feeds on cattle, causing skin lesions, chronic blood loss and transmission of disease-causing parasites. The costs of preventing and treating disease and loss of some cattle are considerable in many parts of the world.
Some ticks have developed resistance against currently used acaricides, the tick equivalent of insecticides. To develop alternative strategies that can better protect cattle, such as vaccines, scientists need to better understand tick infections at the molecular level. For example, scientists already know that tick saliva suppresses the immune response in cattle, facilitating the transmission of tick-borne parasites, but the exact process has not been fully clarified.

The Asian blue tick with its eggs.
Infectious disease veterinarian Satoru Konnai and scientists at Hokkaido University in Japan and colleagues in Brazil investigated what happens to immune cells when they are exposed to tick saliva. The team found that substances in tick saliva, likely a lipid compound called a prostaglandin, increase the expression of two specific cellular membrane proteins on some immune cells. The interaction of these proteins, called programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), leads to the suppression of an immune cell called helper T cell (Th1). This means that the cattle's immune response is less able to combat invading tick-borne parasites.
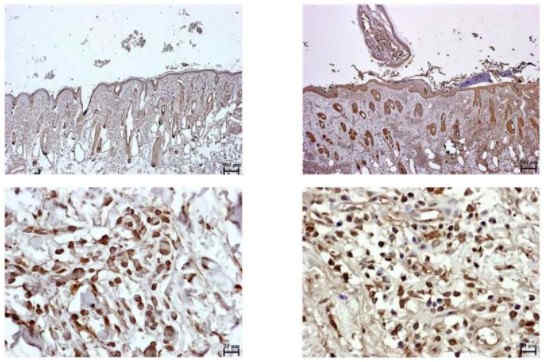
Immunohistochemical staining of PD-L1 in tick-nonattached (left) and tick-attached (right) sites on cattle. An increase in PD-L1 positive immune cells (visually, an increase in the amount and intensity of brown areas) was observed in tick-attached sites.
Further investigation showed Asian blue tick saliva contains a high concentration of prostaglandin E2, which is known to induce PD-L1 expression. However future studies need to confirm if prostaglandin E2 plays a direct role in suppressing the cattle immune response. Also, since this study involved cells in the laboratory, the team says further research in live cattle is needed.
Click here to see more...