By Dana Cronin
Many researchers have looked at nitrogen pollution hotspots around the country. But a new first-of-its-kind, multi-year study from the University of Vermont looks at areas where nitrogen pollution reduction is most feasible without affecting crop yield.
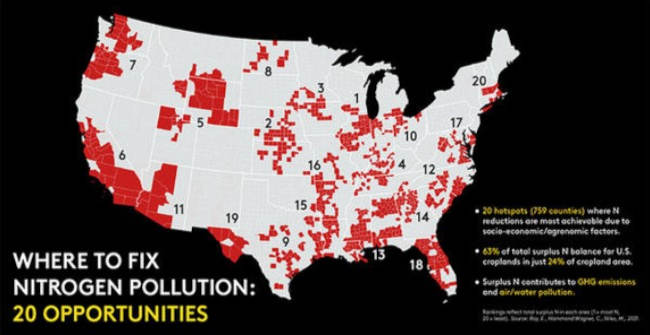
A new study finds that many states in the Midwest have the unique potential to reduce nitrogen pollution without hurting crop yield.
Nitrogen is essential to plant growth and is a major component of most commercial fertilizers. However, excess nitrogen can contribute to environmental degradation, including reducing air and water quality.
“It's a very critical element. There's been people working on managing it better for a long time,” says Eric Roy, an assistant professor at the University of Vermont and a co-author of the study. “But despite those efforts, we continue to struggle to use nitrogen efficiently in food production to get the benefit of growing food without the environmental cost.”
Roy and his team -- including Meredith Niles of University of Vermont and Courtney Hammond Wagner of Stanford University -- looked at areas where nitrogen use is unnecessarily high, meaning farmers can likely reduce their nitrogen use and still maintain their crop yield.
But it’s a tricky thing to balance.
“Reducing it too much comes at a risk for the farmer, a yield loss, also a risk for food security, a loss of food and then in the system,” says study co-author Meredith Niles. “We know there are opportunities to make reductions, but it's such a complicated human decision to weigh those different risks.”
And yet, the team was able to identify 20 “hotspots of opportunity” for nitrogen reduction -- many of which are located in the Midwest.
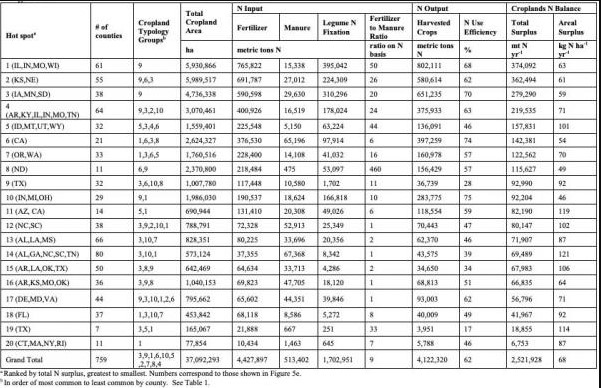
The study found that Midwestern states, especially Illinois, Indiana, Missouri and Wisconsin, had the most potential for tackling farm nitrogen.
The top hotspot stretches across 61 counties in Illinois, Indiana, Missouri and Wisconsin. Next is a 51-county area across Kansas and Nebraska, followed by 38 counties across Iowa, Minnesota and South Dakota.
While the Midwest is an agricultural mecca, that’s not why it stands out in the results. It’s because nitrogen isn’t being used efficiently in the region, the authors say.
“We see nitrogen inputs at a level that suggest they're higher than they need to be relative to other counties producing the same crop mix,” Roy says.
The study also employed social science and took into account agronomic, environmental, social, demographic and economic factors in order to determine the best places to tackle farm nitrogen. By linking nitrogen balance with factors like belief in human-caused climate change, the study concludes there’s more at play than just environmental factors in determining nitrogen hotspots.
“It's not just about the environmental conditions or the soils or the precipitation, but also some of these social factors that are also important in terms of nitrogen management,” Roy says.
Click here to see more...