The development of new urban agriculture technologies, such as vertical and smart farms, has accelerated rapidly in recent years. These technologies are based on hydroponic cultivation in which plants are grown using nutrient-rich solutions rather than soil. Approximately 20-30% of the nutrient solutions used during hydroponic cultivation are discharged without being absorbed by the crops, and because most farmers in South Korea do not treat the discharged solutions, hydroponic farms contribute significantly to environmental pollution.
This problem can be reduced if hydroponic farms use a recirculating hydroponic cultivation method that reuses the nutrient solutions after sterilizing them with ultraviolet (UV) light, instead of discharging them. However, two main issues complicate the implantation of such recirculation systems. First, the potential for diseases and nutrient imbalances to develop owing to microbial growth in the recycled nutrient solutions must be eliminated. Second, the initial investment required to set up a recirculating hydroponic cultivation system is often prohibitive, costing hundreds of millions of Korean won per hectare.
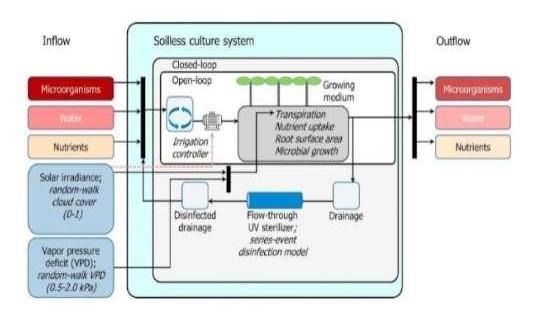
However, a new study conducted by researchers at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)proposes a method that can stably manage the microbial population in recirculating hydroponic cultivation systems. The research team, led by Drs. Ju Young Lee and Tae In Ahn of the Smart Farm Research Center, KIST Gangneung Institute of Natural Products, conducted an integrated analysis of the microbial growth characteristics by constructing a model that simulates the flow of water and nutrients, and the inflow, growth, and discharge of microorganisms in recirculating and non-circulating hydroponic cultivation systems. Their simulations revealed that the microbial population in recirculating hydroponic cultivation systems can be controlled by adjusting the UV output and the water supply. On the contrary, in non-circulating hydroponic cultivation, the microbial population fluctuates considerably depending on the amount of water used, increasingly sharply if there is too little water.
High cost has restricted the use of UV sterilization systems in hydroponic farming in Korea And prompted the research team to develop their own UV sterilization system, with further studies underway to commercialize this system as an economical alternative to imported systems.